Prostatitis is the most common urological pathology for men of reproductive age. According to surveys, every third experienced symptoms at least once in his life, which can be interpreted as inflammation of the prostate gland. Despite such a high occurrence of the pathology, prostatitis remains a poorly examined disease.To this day, there is no consensus that it becomes an output factor for inflammation, since it is possible to distinguish the pathogens from Stis's pathogens in just 10% of the patient's genitarian tract.

The lack of clear diagnostic criteria and characteristic signs of the disease make the accounting of patients more difficult. The symptoms of prostatitis are so non -specific that every doctor interprets it with a large part of subjectivity and can attribute a completely different pathology. Accordingly, the approach to treatment varies and often patients hike from one hospital cabinet to another for years without positive dynamics. Prostatitis deprives a man of trust in his sexual strength, put up his thoughts into a problem and does not bring him as much physically and psychoemotional suffering.
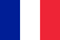
What is a prostate and why is it needed?
The prostate (prostate) is a small glandular organ of a man who is around the urethra below the bladder. It wakes up the urethra and forms one of its sphincter - a muscle book that is supposed to hold the urine. In its shape and size, the prostate of a chestnut nut, with whom it is often compared with anatomists. The part of the urethra that runs in the gland is referred to as prostate. The rear convex part of the prostate is in contact with the rectum, so that it can easily feel with a rectal finger examination. The front surface of the gland lies close to the pubic joint and is associated with moving connective tissue tapes, and the venous plexus lies between them.
The prostate gland consists of lobes, each made by alveoli - small pockets that are lined with secretoric epithelium. The alveoli are connected by the output channels in the form of tubes that merge, enlarge and ultimately fall into the Simpleetle part of the urethra. In the secretion bags, prostate juice is synthesized and accumulated, including nutrients for spermatozoa. It enables male sex cells to maintain its activity in the female body for up to 5 days, which significantly increases the likelihood of fertilization.
The enlightenment of the gland occurs at the time of ejaculation. Prostate juice is mixed with the secret of the testicles and accounts for 10 to 30% of the final sperm volume. Therefore,The prostate gland performs 2 main functions in a man's body:
- Participates in the urine - holds the urine when the muscle fibers are reduced and handed over freely when they are relaxed.
- Offers the livelihood of sperm and distinguishes nutrient prostact juice in ejaculation.
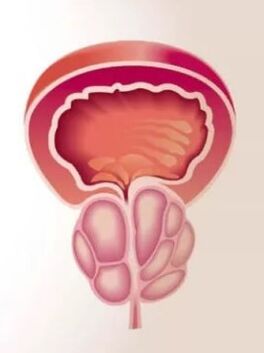
What does the disease develop?
Prostatitis are inflammatory changes in the prostate gland and it should be understood that they arise not only under the influence of bacterial microflora.The causes of inflammation can be all factors that lead to damage to the gland's tissue and the destruction of their cells.
As in any other tissue, the inflammatory process in the prostate is carried out by certain phases:
- Change - damage to the prostate cells.Cytoplasma corns, fragments of the cell nucleus and the remains of membranes come from the destroyed cells into the intercellular space - all are an emergency signal for the immune system. Immunity cells actively strive for the lesion and penetrate from blood vessels and connective tissue. They throw biologically active substances to the place of the damage, under whose influence the blood vessels expand and the "reinforcement" of the cell comes.
- Exudation - the release of the liquid part of the blood from the vessels.Under the influence of immune cells, the walls of the extended vessels for plasma are permeable and plunges into the lesion of the damage. If it is located on the surface of a hollow organ or a high channel of the gland, the liquid part of the blood is released into its lumen. If the inflammation is tissue, swelling is formed. Such a measure is necessary to limit the focus of the damage and prevent the further spread of the pathogen.
- Proliferation is the replacement of damaged cells by similar or connective tissue.The proliferation mechanism is started a little later than the events described above, and its course depends directly on the depth of the damage. Small supply of destruction of the tissue of the prostate are replaced by the same functional cells and the organ completely restores its work. Deep diseases are permitted by scars - the replacement of the dead tissue with connective tissue elements. Chronic prostatitis can ultimately become a complete atrophy of the prostate and the change in their secretor tissue to the kicatricial.
For the proposed reason, prostatitis is divided into:
- Acute bacteria- Pathogenic microflora causes serious damage to prostate tissues with a pronounced inflammatory reaction. Most of the time it develops with an infection with gonococci and other pathogens.
- Chronic bacteria-The association of pathogenic or conditional pathogenic bacteria causes sluggish inflammation, the activity of which remains more than 2 months. As a rule, the pathogens streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella, Mycoplasma, urea, chlamydia, herpes virus and yeast -like fungus of the candidate.
- Chronic -sanctuary- In the presence of an inflammatory process in the prostate, it is not possible to prove a causal microflora. A similar form of the disease develops when urine is thrown into the channels of the prostate, stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis, violation of its emptying (rarely or too frequent ejaculation). In the latter case, the disease is referred to as stagnant prostatitis.
How manifests the disease?
The easiest way to diagnose acute prostatitis,which takes place with signs of poisoning and a pronounced inflammation. In a man, the temperature rises sharply to 38-39 degrees C, pronounced pain in the perineum in the rectal area. You can give the penis in the groin area in the testicle and be so unbearable that the everyday activity of a man is sharply disturbed. In some cases, the body temperature measured in the axillary cavity does not cross the normal indicators, but the rectally is 1-2 degrees per normal value. Signs of prostatitis also become a violation of urination: severe inputs that it is impossible to curb either an acute delay in urine due to a severe edema of the gland. Sometimes defecation becomes painful because the size enlarged in size puts in the lumen of the rectum.
Chronic prostatitisIn its manifestations, it is so diverse that it can easily be confused with a different pathology. In the most typical cases, the symptoms of prostatitis are presented:
- Pain in the crotch, pelvis.It is difficult for the patient to determine a certain place where it is located, often pain in the bar, scrotum, head and rear of the penis and pregnancy spreads. His severity can be different: from the barely distinguishable to intense stupid or pull. Pain is often associated with urination or ejaculation, occurs at the end or at the beginning of the process.
- Violation of urination- The patient often has an urge to empty the bladder, he has to get up repeatedly to urinate. However, the pressure of the beam is normal, the urinary retention rarely develops.
- Sexual disorders- Against the background of constant discomfort in the crotch of a man, an erection deteriorates and self -confidence disappears. Violations are tightened when the pain is associated with the moment of ejaculation: the patient cannot relax completely because he expects unpleasant sensations.
As a rule, the general borehole of a man is not disturbed in chronic prostatitis, and the body temperature is preserved normally throughout the disease.
How is the disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis is determined by the doctoral urologist or andrologistsAfter examining the patient, collecting an anamnesis and examining the symptoms. The doctor must find out the patient's contraceptive method, the presence of STIS in a sexual partner, the possibility of anal contacts without a condom. This data facilitate the diagnosis and guide the doctor's thoughts in the right direction. The prescription of the symptoms of the disease or discomfort in the perineum enables us to assess the course of prostatitis and its severity. The urologist necessarily examines the patient's genital organs and carries out a rectal examination of the prostate gland. To do this, he puts a finger in the back of the patient and gropes the protruding prostate on the front wall of the rectum. Pain and its size indicate the intensity of the inflammatory process.
In addition, the doctor carries out a number of instrumental, microscopic, bacteriological and immunological studies to clarify the cause of the disease. The most common diagnostic method is a 4- or 3 glaze sample. The first method is more difficult to practice in practice, since the patient deliberately interrupts the urination of urination several times. The second modification is easier: the patient continuously urinated in three different containers in equal parts. The first part speaks of the state of the urethra, the second about the pathology of the bladder and kidneys of the third information about the condition of the prostate gland. All collected materials are examined under a microscope. In prostatitis in the third part of the urine, leukocytes and sometimes bacteria are found.
Access to the examination of prostate and massage when collecting secrets
The secret of the prostate gland is also taken for microscopy.For some time, the doctor carries out a prostate massage through the wall of the rectum so that he is emptied into the urethra. Smops are made from the collected material in the laboratory, which is painted and examined with high climb. A sign of inflammation is leukocytes, bacterial etiology of the disease - bacteria in a smear. In order to determine the type of pathogen, the prostatic secret is sown on nutrient media. If pathogenic microorganisms are contained in it, form microbial colonies after 3-5 days, which can then be examined using the bacteriological method that you can receive data on the sensitivity of microflora compared to antibiotics.
From the instrumental diagnostic methods : : :
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Trust of the prostate with Dopplerography - an ultrasonic sensor is inserted into the rectum in order to obtain the best possible visualization of the prostate gland. The blood flow is also evaluated.
- Upsiders rises ugly with stubborn recurring prostatitis. An X -Ray contract is introduced into the urethra, according to which a number of successive images are carried out.

With the treatment of chronic prostatitis, you should prepare for a long fight, as it is not always possible to heal it in a few weeks or even months. It is recommended to combine different methods and instruments for therapy. It is useful to improve drug therapy with households. Regular sex is required for stagnating prostatitis, interrupted sexual acts are unacceptable. The patient's psycho -emotional background is important: depression, depression, problems in personal life and sexual areas are able to negate all efforts of doctors.
How can you prevent?
The prevention of prostatitis includes:
- The use of barrier methods of contraception (condom), especially when it comes to anal sex;
- Timely treatment of STIS;
- Regular sex life, bring relationships with full ejaculation;
- Preventing steps if classes should be used by traumatic sports with all possible protective methods;
- Compliance with personal hygiene;
- Ensure sufficient physical activity.
Despite the fact that prostatitis is not associated with the risk of developing adenoma or prostate cancer today, the disease brings a lot of suffering to its owner. A man who is exhausted by chronic pain, felt his sexual weakness, tired of long treatment, changes noticeably externally and experienced doctors at first glance. In order to avoid such fate, you should be carefully protected with every new partner and treat sexually transmitted diseases in time. Prostatitis is not fully treated in all cases, but an experienced urologist can significantly improve the patient's condition and the quality of his life.